Lifting machine means crane, pully block, monorail, crab, winch, derrick, etc.
Different types of cranes are available. Their selection depends upon the type of use. Jib crane, pillar crane, climbing crane, overhead crane (manual or power-driven), gantry crane, cantilever gantry crane, semi-gantry crane, hammerhead crane, wall crane, etc.
Detailed safety rules for inspection, operation, signaling, and maintenance should be available in writing the operators should be trained for that and they should be strictly followed.
Contents
Overhead Traveling Cranes:
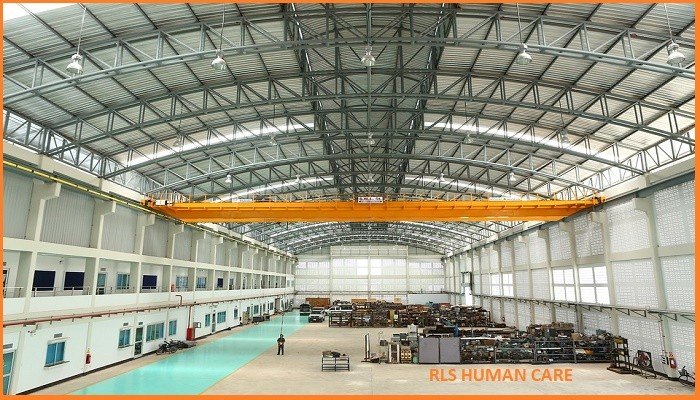

Electrically operated (power-driven) overhead traveling cranes are known as EOT crane. Others are non-powered manually operated overhead traveling cranes. In the use of overhead cranes, great care should be taken for the safe and adequate means of access. It is necessary that all ladders and steps should be provided with secure handholds and footholds. Stairways are preferable to ladders. Proper landing or stages should be provided at the point of transfer from the ladder to drivers cabin.
While any person is employed or is working on or near the wheel track of a traveling crane in any place where he would be liable to be struck by the crane, effective measures shall be taken to ensure that the crane does not approach 6 m of the place. Effective means should be arranged to prevent a crane from traveling into a dangerous zone.
The passageway for crane: The passage (walkway) (50 cm width, toe board 10 cm) shall be provided at a lower level than the crane track and safe access ladders (width >40 cm, double handrails of 90 cm high) shall also be provided at suitable intervals to afford access to these passageways and from passageways to the rails track [Rule 60A GFR]. Vertical head clearance between the walkway and the overhead structure should be more than 2 m. walkway surface should be non-slip type and without floor openings.
Rubber mat at the control panel in the cab is necessary to protect against electric shock. The cab driver should have a full view of the area of work. Rail alignment should be checked every year. Rail stops or bumpers should be so located that when contracted, the crane bridge remains right angle with the runway.
When not in use, a crane should be parked with hook raised at a safer height, all controls in off position and the main switch open.
Inspection and testing of heavy-duty EOT crane include deflection test, overload test, operation test, insulation test, warning light test, earthing and bounding check, hoist and track limit switches check, proximity warning device check, braking, and locking check, control gear check, guarding and weather protection, means of access, buffers and wire ropes of sufficient capacities. All control mechanism, safety devices, leakage in the air or hydraulic system, hooks and ropes, electrical apparatus, travel and steering devices should be properly checked. Preventive maintenance is the most desirable. Moving parts should be regularly lubricated. Crane operators must be fully trained for safe operations.
Deflection test must be carried out with the SWL at rest and with the crab in a central position. The deflection should not exceed 1/900 of the span.
Jib Crane

A jib crane means a stationary or mobile crane in which suspension rope is supported by a projecting, horizontal or inclined member known as a jib crane can lift, lower and rotate the load within the circular area covered by a rotating arm or jib.
It is important that the capacity of the jib crane clearly showing the maximum safe working load for the various inclination of the jib or various positions of the trolly on a horizontal jib should be marked on the sides of the jib or on the mast or the pillars.
A number of accidents have occurred due to overloading of the jib cranes. It should be fitted with automatic indicators which will give efficient sound signals whenever the load moved is in excess of the safe working load.
Structure (Floor, wall or column) should be checked for its strength before mounting a jib crane. The jib should be guyed or braced to withstand heavy load.
A stop plate (bumper) at the end of the jib is necessary to prevent the load trolley from running off the beam. It should be frequently checked.
Bridge and Gantry Cranes
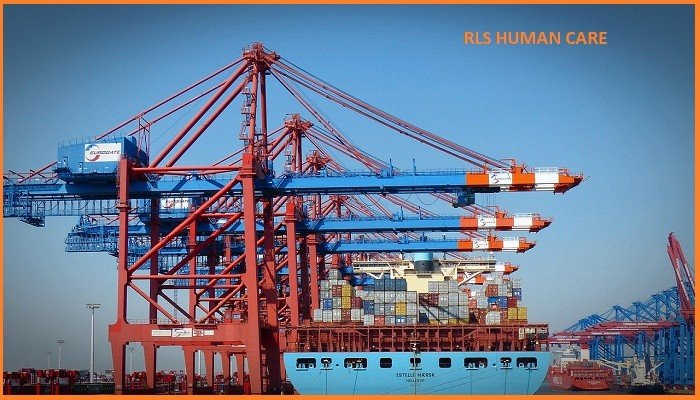

These are similar to traveling cranes except that they run on rails at ground level instead of on elevated runway girders. Gantry cranes have short spans, while the bridge cranes may have spanned up to 100 m or more. Bridge cranes are usually used for handling coal. Sweep guards on nip between rail and wheels, rail clamps and brakes to prevent movement due to high wind, the safe height of electric contact rails, operators cabin to be fireproof and weatherproof, side clearance with the truck wheels of gantry cranes, skew switches to prevent excessive distortion of the bridge etc., are some of the safety measures.
A sounding device should always warn when the crane is moving. The bumpers should be of cast steel plates or spring type. Floor or foot-walk should have drainage, a handrail and toe board up to entrance landing. A rope ladder in the cab for emergency escape and locking ratchets on wheel locks, rail clamps, and brakes to secure against high wind, etc. are necessary.
The general requirement for all crane equipment is good construction, sound material, adequate strength and free from patent defect. It should be regularly inspected and properly used. Statutory provisions must be followed.
Design safety measures should include over travel limit switches, protection of bare conductors control to prevent inadvertent operation load indicators (audio-visual automatic excess load indicator), safety catches, emergency escape, operating position and marking of SWL.
Safe operating techniques must be taught to the operator.
Lifting accessories – chain, wire rope or fiber rope sling, eyebolts, shackles, and special lifting equipment must be of good construction, sufficient strength, properly designed and certified by a competent person as per factory Act 1948 section 29.
Pully-block or Chain Hoists
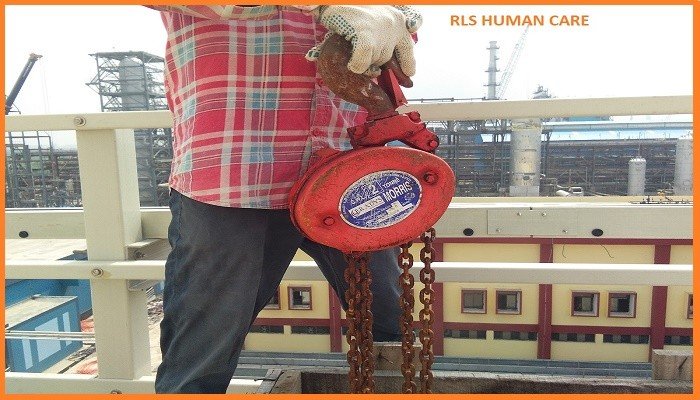

These are spur geared, screw geared and differential chain hoist. They may be portable, portable but permanently hooked onto a monorail trolley or built into the trolley as an integral part. They are suitable for many operations on which a block and tackle fitted with manila rope is used and are stronger and more dependable than rope tackle.
The spur geared type is the most efficient. Screw-geared and differential hoists are self-locking to automatically hold a load in position. Load-carrying parts should be made of steel. The load safety factor of chains should be more than 5. It should be more than 10 for manila rope.
While using pully block in confined spaces, the whole block or the rope or wire nip should be guarded.
The safe working load should be plainly marked on the block and it should be tested every year. All parts subject to wear should be frequently examined.
Monorails Hoists

This system consists of one or more independent trolleys supported from or within an overhead track from which hoists are suspended. Monorail hoists are used to raise, lower and transport materials. They are of three types – hand-operated, semi hand-operated and fully power-operated and fully power operated. Rail stops at the ends of monorail tracks are desirable. Tracks and their supports must be checked the strength and smooth running.
Crabs and Winches
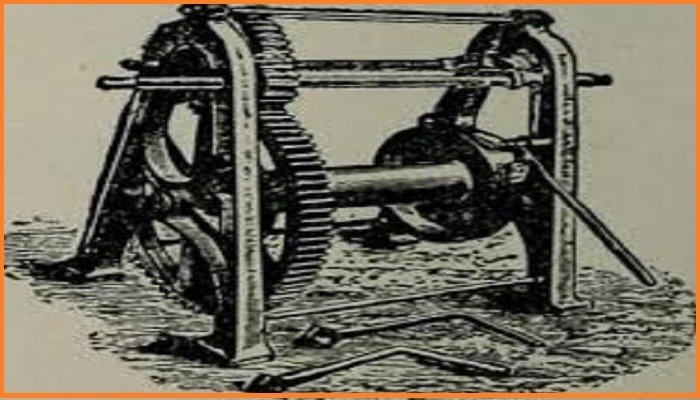
They may be hand operated or electrically driven. Portable crabs and winches must be securely anchored against the pull of the hoisting rope or chain. A dog to lock the gears and a brake or safety lowering devices, crank-pin, lever on pawl and gear guards are necessary. Barricade guards are necessary to protect the operator against breaking wire and recoil of broken ropes.
Derricks

Main types are the stiff-leg, A-frame, guy, gin-pole and the breast derrick. Every part should be firmly anchored. Striking from mast, boom, sill, pully block and swivel hook should be prevented. The hoist engine should be firmly tightened with the base to prevent its pull out. Derrick foot must be firmly supported. For safe rigging of derrick and its gear, rigging plans should be available.
Also, read this
- Mobile crane
- 24 safety checks to perform before putting your crane in operation
- Hydra crane safety
- Eot crane safety
- SWL (Safe working load & Safety Factor)


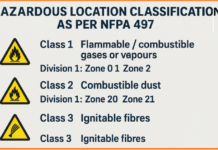

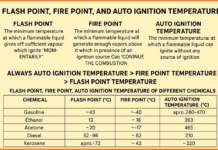
Please send me Sir