Contents
HAZARD, RISK & VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS
Hazards Identification
- Chemical Identity
- Location
- Quantity
Nature of Hazard
Likelihood of a Release occurring Severity of the Consequences
Vulnerable Analysis
- Vulnerable Zone
- Human Population
- Critical Facilities
- Environment
What is Hazardous Area:-
A Hazardous Area is considered to be an area where an explosive atmosphere is or maybe expected to be present which requires special precautions to be taken for the construction, installation and use of electrical equipment.
Combustion Principle:-
WHAT IS VULNERABILITY
Three basic conditions must be satisfied for a fire or explosion to occur:
- A flammable, liquid, vapor or combustible dust must be present in sufficient quantity.
- The flammable liquid, vapor or dust must be mixed with air or oxygen in the proportions required to produce and explosive mixture.
- A source of energy must be applied to the explosive mixture.
- Flammable gas/vapor risk:-
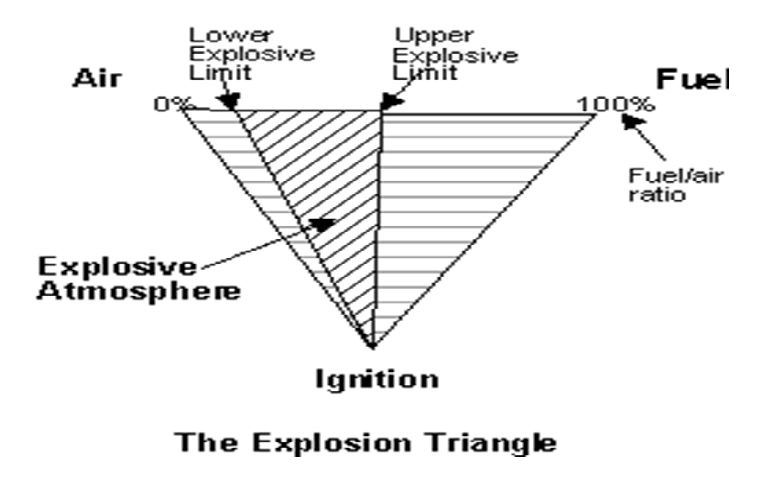
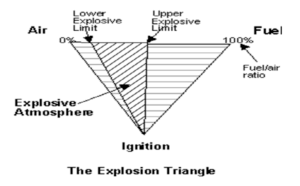
- The lower explosive limit (LEL) is the lowest concentration of the gas in air which can cause an explosion.
- The upper explosive limit (UEL) is the maximum concentration of the gas in air beyond which no explosion can take place. An explosion can take place only between the LEL & UEL.
Ignition Temperature:-
The ignition temperature of a compound is the minimum temperature under prescribed test conditions at which the compound will ignite and sustain combustion when mixed with air at normal pressure, without initiation of ignition by spark or flame.
Sources of energy:-
The different sources of energy can be effectively grouped in three categories:
- Flames.
- Sparks-electric
- Hot surfaces.
Sources of Ignition:-
The following potential ignition sources have been identified:
- electrical arcs and sparks
- flames
- hot surfaces
- static electricity
- mechanical impact
- mechanical friction
- compression ignition
- electromagnetic radiation including optical frequencies
- ionizing radiation
Extent of Zone:-
The extent of Zone is affected by following chemical & physical properties:
- Release rate of gas or vapor
- Geometry of the source of release
- Release velocity
- Concentration
- Volatility of flammable liquid
- Liquid temperature
- Lower Explosive limit
- Ventilation
Determining Hazardous areas:-
- Four essential questions need to be asked
- What is the emission level of the source?
- What type of opening does the source have?
- What is the ventilation availability?
- What level is the ventilation?
Risk:-
Risk is based on the probability that an event will occur times the consequences associated with that event.
Risk = Probability X Consequences
If either the probability or the consequence is zero, then the risk is zero.
What is a Source?
There is probably no greater area of discussion and disagreement than what constitutes a source of release when performing area classification analysis.
Risk:-
Risk is defined as the product of Probability times Consequences.
If, for simplification, we equate the consequences of death to that of a small explosion, then we would conclude that the fire and explosion risks associated with the release of 10 gallons, or even 100 gallons, of hydrocarbon, is within commonly accepted risks (e.g., driving a motor vehicle).
Risk of Emissions:-
After comparing the results of many different dispersion models to existing area classification recommendations it can be concluded that the lower threshold of release for area classification purposes should be in the magnitude of 3 to 5 gallons per minute.
Indian Standards:-
- IS – 5572 (Part I) Classification of Hazardous Areas (Other than mines) for electrical installations.
- IS – 9570 Classification of flammable gases or vapors with air according to their maximum experimental safe gaps and minimum igniting currents.
- IS – 13346 General Requirements for electrical apparatus for explosive gas atmospheres.
- IS – 5571 Guide for selection of electrical equipment for hazardous areas.
- IS – 13408 Code of practice for the selection, installation and maintenance of electrical apparatus for use in potentially explosive atmospheres (other than mines and explosive processing and manufacture)
- IS – 2148 Specification for flameproof enclosures of electrical apparatus.
- IS – 6381 Specification for construction and testing of electrical apparatus with type of protection “e”.
- IS – 5780 Specification for intrinsically safe electrical apparatus and circuits.
- IS – 8289 Specification for electrical equipment with type of protection “n”.
- IS – 2206 (Part I to IV) Specification for flameproof electric lighting fittings.
Vulnerability Analysis:-
Estimate vulnerable zone for screening using credible worst case assumptions
- Determine rate of release to air using information from the facility concerning quantity likely to be released from a vessel or interconnected vessels and fixed assumptions about time of release.
- Identify characteristics of human population (e.g.. Number, concentration. General health ) within estimated vulnerable zone.
- identify critical facilities within estimated vulnerable zone.