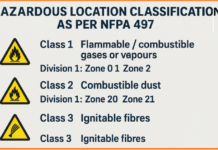
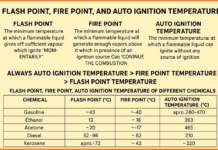
OHSAS 18001 and ISO 45001 are both international standards for occupational health and safety management systems. While OHSAS 18001 was widely adopted, it has now been replaced by ISO 45001, which is a more modern and robust standard.
Here’s a comparison of the two standards:

OHSAS 18001 (2007)
- 4.3 Hazard identification, risk assessment, and control
- 4.4 Legal and other requirements
- 4.5 Objectives and programs
- 4.6 Resources, roles, and responsibilities
- 4.7 Planning and operation
- 4.7.1 Hazard identification and risk assessment
- 4.7.2 Legal and other requirements
- 4.7.3 Objectives and programs
- 4.7.4 Resources, roles, and responsibilities
ISO 45001 (2018)
- 5.1 Leadership and worker participation
- 5.2 Policy
- 5.3 Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities
- 5.4 Planning
- 5.4.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities
- 5.4.2 Objectives and performance indicators
- 5.5 Support
- 5.5.1 Resources
- 5.5.2 Competence
- 5.5.3 Awareness
- 5.6 Operation
- 5.6.1 Planning and control
- 5.6.2 Management of change
- 5.7 Performance evaluation
- 5.7.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and performance evaluation
- 5.7.2 Evaluation of compliance
- 5.7.3 Internal audit
- 5.8 Improvement
- 5.8.1 Incident, nonconformity, and corrective action
- 5.8.2 Continual improvement
ISO 45001 has a more robust framework, aligning with other ISO management system standards (like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001). It emphasizes leadership, worker participation, and risk-based thinking, and includes some new requirements, such as:
- A stronger emphasis on leadership and their responsibilities
- A greater focus on worker participation and consultation
- A more comprehensive approach to risk management
- A shift from a purely compliance-based approach to a more proactive, risk-based approach
Keep in mind that ISO 45001 replaced OHSAS 18001 in March 2021, and organizations were given a 3-year transition period to adapt to the new standard.