Contents
SCAFFOLDING
Scaffolding other names- Scaffold, Staging.
Scaffolding is a temporary elevated platform that supports man, material, and equipment in construction and maintenance activity its made by the metal tube with support by Scaffolding clamp.
Reference:
Scaffolds and Ladders – Code of Safety IS 3696 (Part-1), IS: 2750, IS: 4014(Part & Part II ).
Associated Hazards with Scaffolding:
Use of unsuitable or faulty materials, inadequately supported scaffolding board, Inadequate or irregular platform width, omission of guardrails or toe boards, failure to secure scaffolds, faulty alterations without approval, unsecured ladder slip, misuse of couplers, Overloading of platforms and scaffolds, unsecured ladder slip, fire due to welding/gas cutting in the scaffold, falling object, falling of person, protruding nail injuries, hit by exposed parts of scaffolds, overhead electric lines, sinking of scaffolds, hot gas, steam hazard, etc.
Competent person – One who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surroundings or working conditions that are unsanitary, hazardous, or dangerous to people, and who has the authorization to take prompt, corrective measures to eliminate them.
Qualified person – which has a degree, certificate or professional standing by a recognized institute or college or who has extensive knowledge, training, and experience, who is the ability to solve or resolve problems related to the subject matter, the work, or the project.
Procedure: Scaffolds are intended to provide safe working positions at elevations. Therefore all scaffolds shall be designed, erected, accessed and used to ensure the safety of the people working on the scaffold as well as the workforce around. As the scaffolds are erected and dismantled by manual means, the safety of the workmen engaged for erection and dismantling shall also be ensured.
Erection and Dismantling of Scaffolding:
- Erection and dismantling of scaffolding and staging shall be considered as construction activities and SOP/SWP to be prepared and approved by a competent person.
- Six-directional hazard analysis shall be carried out and mitigation measures shall be covered in SOP/SWP.
- Erection and dismantling sequence shall be planned in such a way that at every stage of erection or dismantling the structure remains stable.
- Following associated hazards are to be addressed during the planning stage:
- Scaffolds shall be erected on a sound base to prevent the collapse of scaffolding due to the subsidence of soil. If needed due care shall be taken to stabilize the soil before erection. No scaffold shall be erected on loose soil and on mud.
- Care shall be taken to ensure that no un-insulated electric wire exists within three meters of the working platform, gangways, and runs of the scaffold. While carrying bars, rods, or pipes of any kind of conducting material of length greater than three meters, in the vicinity of electric wires, special care shall be taken that these do not touch the electric wires.
- For erecting a scaffold near HT line, Rail track, confined space, and gaseous area, clearance shall be taken from an authorized person.
- Care shall be taken to see that no part of a scaffold is struck by a truck or other heavy moving equipment. If required, the movement of the construction vehicle near a scaffold shall be controlled by placing a hard and stable barricade at least three meters away from the scaffold and/or by deploying flagmen.
- No material shall be dumped against scaffolds.
- Scaffolds on the route fares than provided with warning lamp or light, if general lamp/lighting is not sufficient to make it clearly visible.
- Access to emergency resources such as fire alarms, cable tunnels, hydrants, etc., must remain clear at all times. Care should be taken for underground cables and equipment when parts of scaffolds or other fasteners have to be driven in the ground.
Classification of Scaffolds (Scaffolding):
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 TYPES OF SCAFFOLDING
Configuration wise mostly used scaffolds can be classified as follows:
- Independent Scaffolding / Double Pole: this consists of two rows of vertical members connected in both directions making a framework.
- Connected scaffolding / Single Pole: This consists of a single row of vertical and horizontal members connected with the existing structure by means of horizontal connectors/cross members.
- Mild Steel, Tubular / Structural Scaffolding (suspended scaffolding): This type is designed as a modular system for sturdy and repetitive usage.
- Mobile Scaffolds- this consists such a movable and constructed to light duty.
Based on the type of joints, Independent scaffolds, connected scaffolds, and Structural scaffolds can be classified as follows:
Tube and Coupler System: This system is commonly used inside industrial Works. As the stability of this type of scaffolding structure largely depends upon the skill and experience of the erecter and condition of the couplers, nuts and bolts, this type of system is not to be used. However, couplers may be used for fixing the diagonal bracing system or struts.

Cup lock System: This system is used for ease of erection and stability of the scaffold structure. Also, this type of connection provides some moment field which may not be seen at the other scaffolding systems this type of system may be used for scaffolding.

Ring lock System: This type of system is also quite safe and easy to erect. Many scaffolding agencies like DOKA are providing this type of system. This type of system may also be used for scaffolding.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 SCAFFOLDING CAPACITY

Rosette system: Rosette scaffold system is the modular reinforcement scaffold for efficient work.

- The units are stable.
- One system for all areas.
- Easy – Quick & Safe.
- Gravity lock.
Kwik-stage System: This system is not so used and also the flexibility is less compared to Cup lock system and Ring lock system. This is the least preferred.
Load wise scaffolding can be classified as
- Light Duty 1.50kN/m2 150Kg/m2
- General Purpose 2.0kN/m2 200Kg/m2
- Heavy Duty 2.5kN/m2 250Kg/m2
Design of Scaffold:
- The scaffolding agency designer is responsible for the safe design of the scaffolding system.
- The scaffold is generally designed to carry vertical loads and not for horizontal loads. Scaffolds and their components shall be capable to take at least four times the maximum intended load without failure.
- While designing, care shall be taken to ensure lateral stability of the scaffold by adequate provision of horizontal and vertical bracings, struts, guy ropes etc., as required.
- Scaffolds are to be rigidly connected with building or other structures unless the scaffold is so designed and constructed to ensure stability without such connection.
- Every structure and appliance used as a support for a scaffold shall have a firm footing or be firmly supported.
- Uprights of a scaffold shall not be supported on loose bricks, boulders, concrete blocks, paver blocks.
- The use of barrels, boxes, loose tile/brick blocks, pipes or other unsuitable objects as supports for working platforms is not permitted.
- Conditions of supporting ground or structure shall be considered.
- Mobile scaffolds shall be designed with due regard to stability while working on a firm and even surface, and not on a sloping surface. It should be adequately secured to prevent movement when any person is working upon it or upon any ladder which is supported by the scaffold and moved only by the application of force at or near the base.
- The design shall be carried out as per the relevant Indian Standard or by any International standard.
- Erection and dismantling sequence shall be prepared by the designer.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 NEAR-MISS RELATED TO SCAFFOLDING
Parts of a scaffolding system:
Click for types of coupler (Clamps)
Sole Plate: A timber or metal barrier to distributing the load from a standard or base plate to the ground and prevents the sinking of the scaffold. The width and thickness of a timber sole plate shall be 200mm and 25 mm minimum. In place of timber soleplate, 10 mm thick steel plate or steel channel of size more than 200mm depth (ISMC 200) with flanges facing upward, may also be used as the soleplate.
The soleplate area shall not be less than 1000 sq.cm. Sole plates should be long enough to hold at least two vertical pipes and should extend 600 mm beyond the vertical pipes. Sole plates may be avoided in case the scaffold is erected on the firm ground like the concrete floor.
Base Plate: All uprights or standards of a scaffold are to be mounted on a steel base plate. The thickness of the steel base plate shall be a minimum 6mm and size shall be of 150 mm x 150mm. Irrespective of the supporting ground condition or concrete surface, the base plate is to be used mandatory.

Upright – Standards: Uprights or Standards are the vertical members of a scaffold and are to be mounted on steel base plate. These should not be placed more than 3 m apart and remain vertical to avoid any additional moment.
Uprights shall be in good condition without any kink or bend. Uprights are fitted with the fixed lower cup at an interval of 0.5 meter and captive rotating upper cup. Standards have 150mm spigots to allow vertical connection of further standards.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 SOP
Horizontal members – Ledgers

Horizontal members or ledgers are connected with the Standards by means of the cup lock system. All ledgers of a cup lock system incorporate symmetrical forged blade ends, making assembly quicker and making components completely interchangeable. Horizontals locate in the bottom cups of the standards and are secured by locking the upper cup.
In the case of the rosette system, horizontal members (ledgers) are connected with the Standards by means of a wedge inserted between the perforated disk and the end-piece of the ledger.
Transoms: These are designed to provide intermediate supports to scaffold boards between inner and outer ledgers.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 HIRA
Working platform.
- All working platforms must be fully decked by competent persons and in good and sound condition.
- Platform units may be individual scaffold-grade wood planks or fabricated scaffold platforms.
- Corrugated sheets, plain steel sheets or steel gratings of any kind shall not be used for the working platform.
- Steel chequered plates may be used with adequate stiffening.
- The platform should be closed boarded, overlapping of boards and excessive overhangs should be avoided.
- There should not be any opening in the platform except for allowing access to such a working platform. All openings, if required for access, shall be guarded by means of hand-rail, mid-rail and toe guard along three sides and a suitable steel gate on the entry side.
- Every working platform shall be a minimum 600 mm wide when used for persons only and not for materials; the Minimum width of a working platform is 800mm when used for the person and for the deposition of construction materials like bricks.
- 430 mm wide platforms are, however, permitted on ladder scaffolds, folding trestle scaffolds, slung scaffolds in the vicinity of a roof and suspended scaffolds when the work is light and of short duration.
- The space between the edge of the working platform and the face of the building shall be as small as practicable. Where workmen sit on the edge of the platform to do their work, space not exceeding 300 mm may be permitted.
- Every board forming part of a working platform shall afford adequate security having regard to the distance between horizontal connectors and other supports;
- Scaffolding boards shall not project beyond its end support by more than 4 times the thickness of the board unless it is effectively secured to prevent tipping;
- Every board or plank shall rest securely and evenly on its supports; have at least 3 supports unless it is strong and thick enough not to have excessive sagging.
- Working platforms shall extend, wherever practicable, at least 600 mm beyond the end wall or working face where work is to be carried out.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 SAFE WORKING LOAD
Fall prevention – handrail, mid-rail, and toe guard.
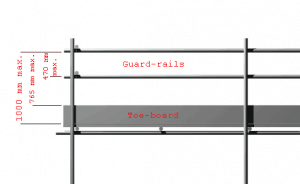
- To eliminate falling hazards, scaffolds must have complete with firm handrails, mid-rail, and toe boards that eliminate the need for fall-arrest equipment.
- Handrails shall be provided at a height of 1.0 meters and mid-rails shall be provided at a height of 0.5 m from the top of the working platform.
- Toe-boards shall be provided all around the working platform and shall be of a minimum of 100mm high.
- Corrugated sheets cannot be used as the toe-boards.
- Do not Fall arrest equipment used as a substitute for handrails, mid-rails, or toe board.
- Slings, wire ropes or manila ropes cannot be used as the substitute for handrail or mid-rail.
Ladder: Portable ladders may be used for flights less than 4.0 meters and fixed ladders should be provided for flights above 4.0 meters.
- Ladders should be placed at an angle of approximately 75° from the horizontal.
- The ladder must be secure with three contacts top, middle, and bottom to prevent displacement.
- Ladder rails should be extended at least 1.0 m above the landing.
- Last top rung of the ladder shall not be above the landing platform.
- Rungs shall be placed at the uniform spacing of 300mm.
- The width of the ladder shall not be less than 300mm.
- IS: 3696 (Part-2) standard ladder shall be used for scaffolding access.
- Ladder scaffolds shall be used only if the work is of such a light nature and the material required for the work is such that this type of scaffold can be used safely.
- Ladders serving as uprights in scaffolds shall:-
- be of adequate strength;
- be placed so that the two sides of each ladder are evenly supported or suspended; and
- be secured to prevent slipping.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 ELECTRICAL SAFETY
Staircase tower scaffolding:

- For access to the working platform at a height of more than 4.0 meters, a staircase tower is preferable, if sufficient space is available to erect.
- A stair tower shall be designed to ensure the lateral stability of the tower for the required standing height.
- Stair tower shall be provided with hand-rail, mid-rails on both sides of the stair.
- The landing platform at each level may be of steel chequer plate or gratings.
Ramps: Every ramp:
- used for man passage then ramp shall be a minimum of 430 mm wide.
- be minimum 600 mm wide if used for passage of materials.
- Not be steeper than 5(H):1(V)
- Ramp units may be individual scaffold-grade wood planks or fabricated scaffold platforms.
- Corrugated sheets and plain steel sheets shall not be used for ramps.
- Steel chequered plates may be used with adequate stiffening.
- There should not be any opening in the ramp.
- Every side of a Ramp shall be provided with:
- guard rail to a height of 1.00 m above the platform.
- Intermediate guard rail at not more than 500 mm height.
- Toe-board of at least 100 mm high.
Erection of scaffolding
- Scaffolding erection must be carried out only by competent persons who are trained for this purpose and have sufficient expertise under the direct supervision of a “competent person”.
- Erection sequence as prescribed by the designer or the manufacturer shall be followed.
- The stability of the scaffold at every stage of erection shall be ensured.
- Before erection, all components of the scaffold shall be inspected. All defective or damaged components shall be rejected and not used for the scaffolding.
- Six-directional hazard analysis shall be carried out and appropriate corrective actions shall be taken.
- PPE shall be used by all engaged for the erection job.
- Adequate fall protection measures shall be taken as per the safety standard on “Working at height”.
- Warning sign “Scaffold under erection” shall be displayed at a prominent position of the scaffold during erection.
- After the erection of a scaffold, all access points shall be barricaded either by RED tape or by the hard barricade, till the scaffold is inspected by a competent person and declared “safe” for use also use a scaffolding tag.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 WORK PERMIT SYSTEM
Use of Scaffolding
- All scaffolds must be inspected by a scaffolding inspector or competent person before use.
- An inspection record shall be generated and signed by the inspector.
- All corrective measures shall be taken by the contractor, as per the inspection record and verified by the inspector.
- Once the scaffold is declared safe, all barricades to the access points of the scaffold will be removed.
- If found safe, a tag with the sign “Safe for use” is to be displayed at a prominent point on the scaffold.
- No one shall use a scaffold without having a “Safe for use” tag.
- Only proper access to be used. No one shall climb the bracing, guard rails, vertical post or other components of the scaffold unless it is designed for the same.
Climb safely on Scaffolding
- Face the rung while climbing.
- Use both hands while climbing a ladder.
- Do not carry materials while climbing
- Keep one hand firmly on the ladder all the time.
- Clean shoes and rungs before climbing, in order to avoid slipping.
- Hold hand-rails while climbing a stair.
- Do not use a mobile phone while climbing.
Work Safely on Scaffolding
- Do not work on a slippery platform.
- Do not work on a platform with the projected nail or unguarded openings.
- Do not work from a scaffolding platform during storms or high winds.
- Do not overload materials on the platform. Materials shall be kept in an evenly distributed manner.
- Do not store materials beyond a reasonable time.
- Do not deposit materials on a working platform with a jerk.
- Do not extend the working height by standing on barrels, handrails, boxes, ladders, or other materials on the scaffold platforms.
- Do not loosen, detach or remove any component of the scaffold.
- Stand only on the platform area. Do not try to extend the work area by leaning out over the hand-rails.
- Anchor the safety lanyard at a height of more than 1.0 meters to any other nearby stable structure.
- The lanyard may be anchored with the hand-rail if no other independent structure is available. The lanyard must not be anchored with the mid-rail or with the working platform.
- Scaffold materials, tools, or other objects and materials including waste material shall not be thrown, tipped, or shot down from a height where they are liable to cause injury. The material shall be lowered down.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 SAFETY INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
Dismantling of scaffolding
- The scaffolding dismantling must be carried out by competent persons who are trained for this purpose and have sufficient expertise under the direct supervision of a “competent person”.
- Dismantling sequence as prescribed by the designer or the manufacturer shall be followed.
- The stability of the scaffold at every stage of dismantling shall be ensured.
- Six-directional hazard analysis shall be carried out and appropriate corrective actions shall be taken.
- PPEs shall be used by all engaged for the dismantling job.
- Adequate fall protection measures shall be taken as per the safety standard on “Working at height”.
- Warning sign “Scaffold under dismantling” shall be displayed at a prominent position of the scaffold during dismantling.
- All-access points shall be barricaded either by RED tape or by the hard barricade, till the completion of dismantling.
Suspended Scaffolding
Every suspended scaffold shall be secure with adequate and suitable chains or ropes and winches or other lifting appliances or similar devices and shall be suspended from suitable outriggers, joists, runways, rail tracks, or other equally safe anchorages.
The winches or other lifting appliances or similar devices of a suspended scaffold shall be
- Provided with a brake or similar devices which comes into operation when the operating handle or lever is released; and
- Adequately protected against the effects of weather, dust, or material likely to cause damage.
The outriggers provided for a suspended scaffold shall be
- of adequate length and strength and properly installed and supported;
- Provided adequate stops provided at their outer ends; scaffold shall be installed horizontally.
- Sufficient spaced having regard to the construction of the scaffold and of the runway, joist or rail track on which the scaffold is carried.
- Where counterweights are used with outriggers, these counterweights shall be securely attached to the outriggers and shall be not less than three times weight which would counterbalance the weight suspended from the outrigger including the weight of the runway, joist or rail track, the suspended scaffold, and persons and other loads thereon.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 RADIATION SAFETY
The points of suspension of every suspended scaffold shall be at an adequate horizontal distance from the face of the building or other structures.
Every runway, joist, and rail track supporting suspended scaffold shall be
- of suitable and sound material;
- of capable and adequate strength for the purpose for which it is used;
- free from patent defect;
- provided with adequate stops at each end.
The suspension ropes or chains of a suspended scaffold shall be –
- securely attached to the outriggers or other supports and to the platform framework or to any lifting appliance or other device attached thereto, as the case may be; and
- kept in tension.
Where winches are used with suspended scaffolds, the suspension ropes shall be of such a length that the lowest position at which the scaffold is intended to be used, there are two turns of rope used on each winch drum and the length of each rope must be clearly marked on its winch.
Every part of a suspended scaffold and all plant and equipment used for the purpose shall be
- of good construction;
- Suitable and sound material;
- Properly maintained;
- Where constructed of metal, free from corrosion.
Adequate arrangements shall be made to prevent undue tipping, tilting, and swinging of a suspended scaffold and to secure it to prevent undue horizontal movement while it is being used as a working platform.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 EXCAVATION SAFETY
If No rope available, other than a wire rope shall be used.
Fibber rope and pulley block may be used provided, the work to be carried out from a Suspended scaffold is of such a light nature and the material required for the work is such that a cradle or similar lightweight suspended scaffold having a platform of not less than 430 mm wide.
If a suspended scaffold is carried on fiber ropes and pulley blocks, the rope shall be spaced not more than 3.20 m apart.
The platform of every suspended scaffold shall
- be closely boarded, planked or plated; and
- be of adequate width to afford adequate working space at every working point and shall, in any event, be at least 600 mm wide if used as a footing only and not for the deposit of any material;
- be at least 800 mm wide if used for the men and deposit of material.
- be acceptable to 430 mm wide if it is the cradle of lightweight.
- not to be used for the support of any higher scaffold.
- be so arranged or secured that at each working position the space between the face of the building or structure and the platform is as small as reasonably practicable;
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 REBAR SAFETY
Trestle or Mobile Scaffolding
- All trestles and supports used for the construction of any trestle/mobile scaffold shall be
- of good construction, suitable and sound material;
- of adequate strength for the purpose for which they are used and free from patent defects.
- Properly maintained.
- A trestle scaffold shall not be used
- if the scaffold is so situated that a person would be liable to fall from its working platform a distance of more than 4.5 m; or
- if erected with more than one platform where folding supports are used.
- trestle scaffold shall not be erected on a scaffold platform unless
- the width of the said platform is such as to leave sufficient clear space for the transport of material along the platform; and
- the trestles or supports are firmly attached to the platform and adequately braced to prevent displacement.

- The erection, dismantling and use of the mobile working areas is only permitted up to wind forces of a 6 km/hrs.
- Horizontal and vertical load effects, which can cause the tip over, are to be avoided.
- The mobile working scaffold must not be lifted and shifted using a forklift or the like.
- The mobile working scaffold must not be moved if there are people or loose objects on the planking surface.
- The castor brakes must be released in order to move the working scaffold.
- Upon movement, the castors are to be again blocked using the Use of Gin Wheel castor Brake.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 NDT SAFETY
Use of caster wheel

- The caster wheel should be supplied with a test certificate.
- Gin wheel rope should be of the correct size to suit the Gin wheel min of 18mm, the rope should comply with the relevant standard and should be supplied with a certificate of conformance.
- Materials should be firmly attached to the rope and should not exceed 50 in weight or the rope Manufacturer’s recommendations.
- The operative responsible for raising or lowering materials should wear a safety helmet and gloves at all times to prevent injuries to the head and to prevent burning injury that could be caused by the use of the rope.
Training for Scaffolding
The employee involved in the erection, dismantling, moving, repairing, etc., of the scaffolding shall receive training from the competent person. The aim of the training is to identify hazards associated with the work in question. Training shall consist of:
- The nature of scaffolding hazards
- The correct method for erecting, disassembling, moving, operating, repairing, inspecting, and maintaining of the scaffold.
- The scaffolding design criteria, maximum intended load wearing capacity, and the intended use of the scaffold.
The employee who performs work while on a scaffold shall be trained by a qualified person so they can recognize hazards associated with the type of scaffold being used and understand the procedures to control those hazards. Training will cover the following topics as necessary:
- Hazards present in your work areas such as electrical hazards, fall hazards, and falling object hazards.
- The correct procedures for dealing with electrical hazards and for erecting, maintaining, and disassembling the fall protection system and falling object protection systems used.
- How to use the scaffold and the proper materials handling technique on the scaffold.
- The maximum intended load and the load-carrying capacities of the scaffolds used.
CLICK HERE FOR 👉 WORK AT HEIGHT SAFETY
Monitoring and reviewing:
Frequency: After the erection of scaffold, weekly and after high wind and rain
Mechanism: inspection by a competent person
Records: inspection report
Responsibility: executing department, consultants, scaffolding agency.






This is a very important training document, with all the necesssary information about scaffolding. please i will wish you kindly send a PDF copy to me.
THANK YOU
Excellent and informative. Your blogs helps me a lot. Good work and keep it up.
I am looking information regarding work on top of tanktainers or containers. Please see if you have something.
This blog contains all the information about scaffolding. Those people who want complete information about it, can get that information with the help of this blog. You have really helped those people who are in searching of contents about scaffolding. I want to thank you for sharing such a useful post. You have done a good work. Keep it up.
Hi sir good evening
A very thankful to you for updating this very useful materials but I have problem .
When I read this I want download also, but no download position
So please do needful sir
Thank you sir.
oK. I will send you a pdf copy of this article.
Excellent post. It’s really a nice and helpful piece of info.This is the perfect blog for anyone. Thanks for sharing this information with us.
Hi