Contents
What is Excavation?
Excavation is any man-made cut on earth by removing soil. It is an essential & major part of construction activities and one of the most hazardous also. Many killed during excavation due to Cave In, bogged down of machine, fall of material & contact with underground services.

Hazards associated with excavation:
- Cave-ins or Collapse of the sides due to inadequate support.
- Fall of people and vehicles into the excavation due to inadequate barriers, warning signs & illumination.
- Water seepage reducing soil strength resulting in the collapse of sides.
- The danger associated with excavation machinery
- The proximity of adjacent buildings or structures and their stability
- Contact with underground services electricity/communication cables, utility pipelines, oil & gas pipelines.
- Lack of oxygen and exposure to a hazardous substance, toxic fumes, flammable gas.
- Asphyxiation by the carbon dioxide that can be present in excavated space caused by lack of ventilation or by exhaust gas of running diesel engines.

Excavation confined space:
Where ever the depth of excavation is more than 1.2 meters shall be treated as confined space because of restricted means of ingress & egress and that is also not designed for normal occupancy. Obtain a confined space permit and fulfill its requirements.

Method of excavation:
- Manual
- Mechanized excavation by excavators

Decide method of excavation considering the following:
- Type of soil which is to be excavated.
- Ground stability.
- Chance of seepage of water.
- Excavation won’t affect the adjoining building.
- Presence of hydrocarbon, utility lines & electrical, telephone cables.
Soil Classification for excavation:
Soil can be classified by visual or manual test
Manual analysis of soil sample is conducted to determine qualitative properties of soil, these are:
- Plasticity
- Dry strength
- Thumb penetration
- Drying test
CLICK HERE FOR ? HIRA AND JSA DOWNLOAD
Here the soil is classified based on unconfined compressive strength that can be determined by a Thumb penetration test, use of pocket penetrometer or Vane shear test.

Before excavation ensures work should be planned, the method of excavation & type of support should be decided.
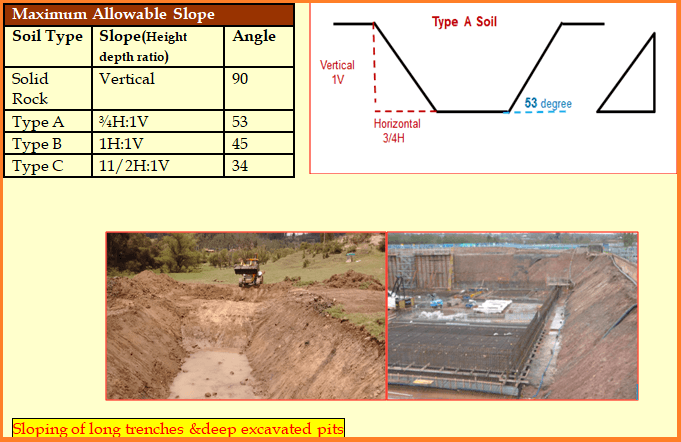
Excavation Trench:
Any excavation in the ground where the depth of excavation exceeds the width (width no wider than 4.5 meters) and depth is more than 1.5m.
Trenching is one of the most hazardous construction operations that pose the greatest risk of a cave-in that claimed many lives every year. It requires a protective system against cave-in or soil collapse.

There are two types of protective systems are available sloping & shoring, the selection will depend on soil type & site feasibility.
Excavation Shoring/Shuttering:
Installing metal sheets or wooden planks with jacks or support against the wall of trench to prevent cave-in or soil collapse. The trench box can also be used.
CLICK HERE FOR ? DUMPER TRUCK SAFETY
Shoring can be done in different ways (i.e. Timber, Hydraulic shoring, shielding or trench box) based on soil condition or trench depth.

You are reading at rlshumancare.com. Do not forget the name RLS HUMAN CARE. Please share with your friends and help RLS HUMAN CARE. Thank You!!
Sloping in Excavation:
If enough space is available, sloping or benching the trench will be providing greater protection against cave-ins or soil collapse without the use of any equipment.
It is a method of forming sides of an excavation that are inclined away from excavation so as to prevent cave-ins.
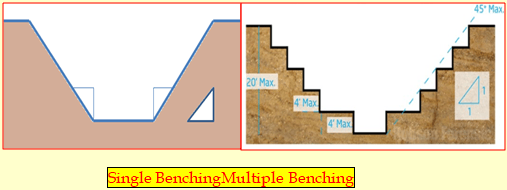
Benching in Excavation:
There are two types of benching single or multiple & it shall be allowed in cohesive soil only.
Prerequisite for Excavation work:
- Visit the location mark the site& prepare the plan.
- Conduct job safety analysis or Hazard identification & risk analysis by a competent person where ever required.
- Access the requirement of machines & tools
- Obtain work permits from authorized agencies & made available at the site.
- Deploy skilled & competent workmen for a critical task.
- Conduct toolbox talk before starting the job.
Tools box Talk on Excavation Safety:
- Give a brief introduction about the job, machine & equipment’s to be used
- Hazards involve in work
- Required PPEs
- Details of rescue & evacuation plan
Safety Rules during excavations:
Rule no 1: Don’t leave the open pit, trench, and excavation site unguarded provide soft/hard barricading, place caution boards & provide warning lamps during darkness.
CLICK HERE FOR ? CONSTRUCTION SITE SAFETY MANAGEMENT

Rule no 2: Barricade at 1m height (with red & white band self-glowing caution board) for excavation beyond 1m depth.

Rule no 3: Provide two entry/exit for excavation beyond 1m depth, travel distance from any point of excavated area to ladder shall not be more than 10 meters.

Rule no 4:Provide safe angle of response 45˚ else shoring/Sloping
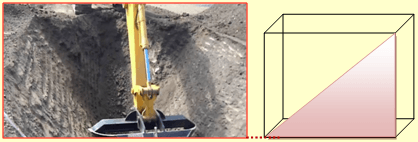
Rule no 5:0.5m width bench at every 1.5m of a deep excavation trench.

Rule no 6:Dump excavated earth/Soil min. 1m away from the lip of trench/excavation site.

Rule no 7:Don’t allow vehicle movement at least 2m from the edge of excavation/trench.

Rule no 8:Avoid excavation during rain.

Rule no 9: All cutting should be carried out from top to bottom, in case of undercutting extra protection must be taken (i.e. Tunnel).

Rule no 10:When mechanized excavator not in operation the machine shall be kept on firmed level ground with mechanical excavator resting on the ground. Wheel or belt shall be suitably jammed to avert any accidental movement.
You are reading at rlshumancare.com. Do not forget the name RLS HUMAN CARE. Please share with your friends and help RLS HUMAN CARE. Thank You!!

Rule no 11:Provide protection against protruding rebars by using rebar caps. REBAR SAFETY
CLICK HERE FOR ? REBAR SAFETY

Other contributing factors which may increase risk during construction
- Involvement of a huge workforce
- Executing the conflicting nature of jobs simultaneously
- Unskilled workforce involvement
- Un-organized jobs
“Learn from others accident don’t wait for your turn”
Excavation cave-ins cause serious and often fatal injuries to workers all over the world this type of incident is a major cause of deaths associated with work in excavations and accounts for nearly 1% of all annual work-related deaths in the world.
Excavation Accident Case Study:
Description:
The worker was constructing a new drain inside the trench in front of the building under construction. While the worker was leveling the surface for a new drain, a wall left behind from the old drain collapse from the side of excavation causing fatal injuries to the worker.

What Went Wrong:
The brick walls were constructed on both sides of the old drain to retain the soil. Before constructing the new drain, the brick wall on one side of the old drain was removed and the area was excavated to facilitate the construction process.
The other brick wall, however, was not removed as it did not pose as an obstruction to the construction of the new drain latter that loosens its strength and collapsed.
Findings:
- Excavation started near the foundation of the old brick wall without providing adequate support to the wall.
- Almost half-length of wall sunk into the excavation. A large amount of soil near the brick wall bottom sunk weaken the wall.
- The brick wall that collapsed onto the deceased worker was about 4 meters long and weighed about 1.6 tons.
- Heavy rain was reported before the incident leading to soil movement and weakens retaining the strength of the wall.
- The contractor did not provide shoring/shuttering & sloping in the trench.

Learning from the accident:
- Know your hazards, identify hazards associated with excavation activity i.e. structure/wall collapse, cave-in, etc.
- Ensure the stability of adjacent structures before the commencement of excavation.
- Conduct comprehensive risk assessment and eliminate & control the risk through detail plans.
- Detailed inspection of site after heavy rain, storm & snowfall in addition to the routine inspection.
- Follow safety guidelines & best practices.
How to avoid recurrence of such accidents:
The audit is an independent examination or evaluation of system & process to check compliance of set of procedures and provide comprehensive feedback.
Pre excavation audit shall be conducted before the commencement of heavy excavation activity it will provide detail information & would be helpful in eliminating potential hazards.
Excavation safety checklist
Also, read this:
HIRA (hazard identification and risk assessment)
You are reading at rlshumancare.com. Do not forget the name RLS HUMAN CARE. Please share with your friends and help RLS HUMAN CARE. Thank You!!





Nice information sir. Thank you so much.
So happy that I found your blog and I absolutely love your information about the excavation safety. I liked and it is wonderful to know about so many things that are useful for all of us! Thanks a lot for this amazing blog!! I agree with all your points that you have stated here, love this blog.
Great information for the protection of personnel associated with excavation and trenching work. A topic that is taken for granted
Hey thanks for posting this useful content on excavation safety presented here, I really hope it will be helpful to many. I hope you keep update us with such great tips and information in future too. This is a great post; I will share as much as I can. Appreciative content!!