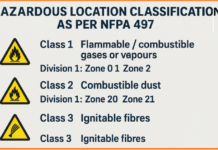
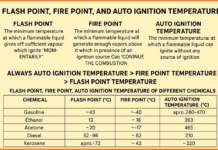
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on safety policies and regulations in India. The government has recognized the importance of ensuring the safety and well-being of its citizens and has implemented various laws and regulations to protect them. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of safety policy laws in India and their significance.
Contents
1. The Factories Act, 1948
The Factories Act, 1948 is a crucial legislation that governs the safety, health, and welfare of workers employed in factories. It aims to prevent accidents and promote a safe working environment. The Act covers various aspects, including the provision of clean drinking water, ventilation, lighting, and sanitation facilities in factories. It also mandates the appointment of safety officers and the maintenance of accident records.
2. The Mines Act, 1952
The Mines Act, 1952 focuses on the safety, health, and welfare of workers employed in mines. It lays down provisions for the prevention of accidents, the use of proper equipment, and the availability of first aid facilities. The Act also requires mine owners to appoint competent persons to oversee safety measures and conduct regular inspections.
3. The Building and Other Construction Workers (Regulation of Employment and Conditions of Service) Act, 1996
This Act aims to regulate the employment and working conditions of construction workers. It mandates the registration of workers and the establishment of welfare boards for their benefit. The Act also emphasizes the provision of safety equipment, medical facilities, and accident insurance for construction workers.
4. The Motor Vehicles Act, 1988
The Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 is primarily concerned with road safety. It lays down rules and regulations for the use of motor vehicles and aims to prevent accidents on the roads. The Act covers various aspects, including driver licensing, vehicle registration, traffic rules, and penalties for traffic violations. It also mandates the use of seat belts, helmets, and other safety measures.
5. The Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020
The Occupational Safety, Health, and Working Conditions Code, 2020 is a comprehensive legislation that consolidates and replaces several existing labor laws. It aims to ensure the safety, health, and welfare of workers across all sectors. The Code covers various aspects, including safety standards, welfare facilities, working hours, and leave provisions. It also introduces the concept of a single registration and a unified compliance mechanism.
6. The Environmental Protection Act, 1986
The Environmental Protection Act, 1986 is an important legislation that focuses on the protection and improvement of the environment. While it may not directly address safety policies, it plays a crucial role in safeguarding the health and well-being of the population. The Act lays down provisions for the prevention and control of pollution, the management of hazardous substances, and the conservation of natural resources.
7. The Disaster Management Act, 2005
The Disaster Management Act, 2005 provides a legal framework for disaster management in India. While its primary focus is on disaster preparedness and response, it also encompasses safety policies. The Act mandates the formulation of disaster management plans, the establishment of disaster response agencies, and the coordination of efforts during emergencies. It emphasizes the importance of ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals during disasters.
These are just a few examples of the safety policy laws in India. It is important for individuals, organizations, and the government to be aware of these laws and comply with their provisions. By prioritizing safety and implementing effective safety policies, we can create a safer and more secure environment for everyone.