Electrical safety is very important in any setting, be it residential, commercial, or industrial. Circuit breakers play a crucial role in safety of electrical systems, preventing damage to equipment, and ensuring the safety of human. There are several types of circuit breakers, each designed to address specific electrical safety needs. In this article, we will explore the various types of circuit breakers and their applications in promoting electrical safety.
Contents
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)

Air circuit breakers use air as the arc extinguishing medium. They are commonly employed in low-voltage applications and find widespread use in industrial and commercial settings. ACBs offer reliable protection against overcurrent and short circuits, contributing to the overall safety of electrical systems.
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)

MCBs are the workhorses of residential and light commercial applications. Found in distribution boards, these circuit breakers protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. Their compact design and ease of installation make them an essential component for ensuring safety in homes and smaller electrical systems.
Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
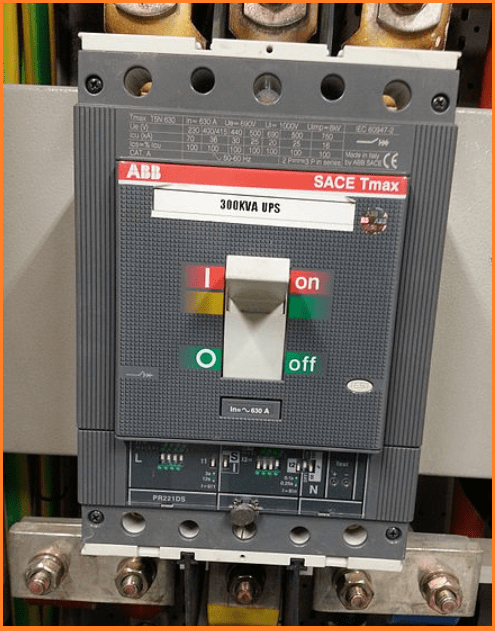
Similar to MCBs but with higher current ratings, MCCBs are commonly used in industrial and commercial installations. These circuit breakers offer adjustable trip settings, providing flexibility in tailoring protection to specific equipment and applications, thus enhancing overall electrical safety.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
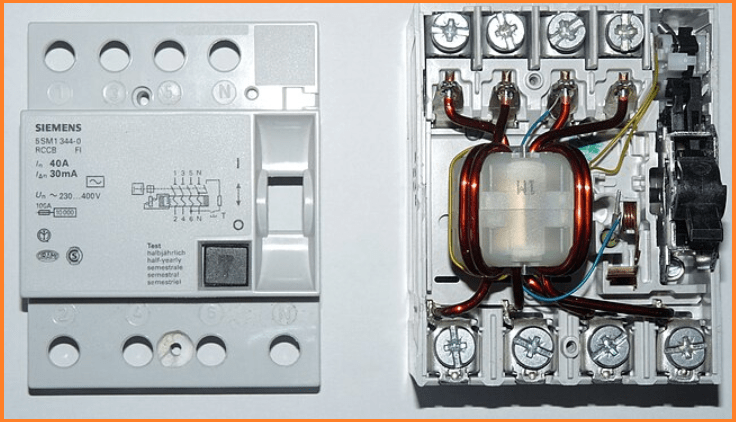
RCCBs are designed to protect against earth leakage currents, preventing electric shocks and fire hazards. Widely used in residential and commercial installations, RCCBs contribute significantly to enhancing personal safety by quickly disconnecting power in the presence of ground faults.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
GFCIs, a specialized type of RCCB, focus on personal protection. Commonly installed in bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor outlets, GFCIs rapidly cut off power when they detect ground faults, preventing electrical accidents and promoting safety in areas where water and electricity may come into contact.
Oil Circuit Breaker

Oil circuit breakers are employed in high-voltage applications and use oil as the arc extinguishing medium. These circuit breakers are critical components in power distribution systems, providing robust protection against faults in the electrical grid.
Vacuum Circuit Breaker

Vacuum circuit breakers utilize a vacuum as the arc-quenching medium. Suitable for medium to high-voltage applications, they are known for their reliability and efficiency. Vacuum circuit breakers contribute to electrical safety by ensuring the quick and effective interruption of fault currents.
Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6) Circuit Breaker
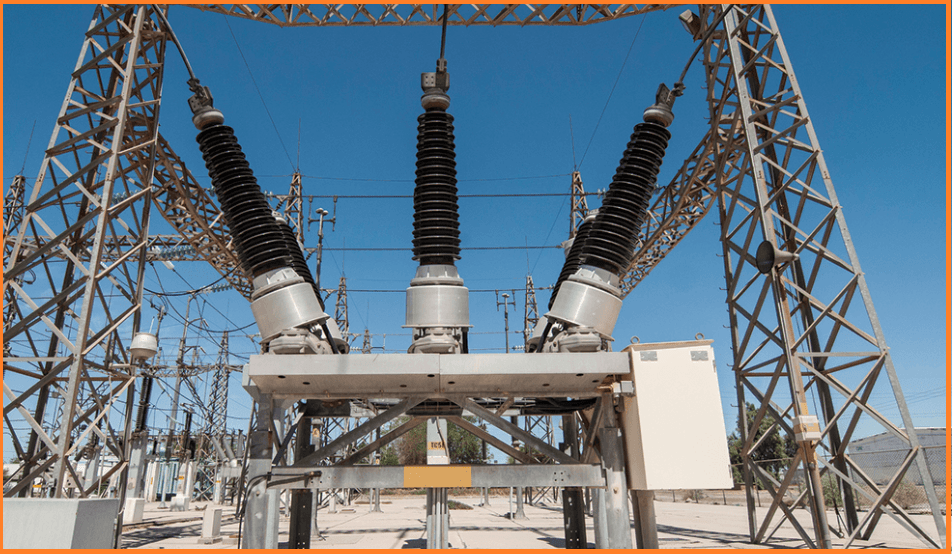
SF6 circuit breakers are designed for high-voltage applications and use sulfur hexafluoride gas as the arc extinguishing medium. They are commonly found in power substations, providing essential protection against overcurrent’s and short circuits in the transmission and distribution of electrical power.
In conclusion, the various types of circuit breakers play integral roles in promoting electrical safety across different settings. Whether in homes, businesses, or industrial facilities, the right circuit breaker helps prevent electrical accidents, protects equipment, and ensures the reliable functioning of electrical systems. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each type allows for informed choices in designing and maintaining electrical installations that prioritize safety. As technology advances, the evolution of circuit breakers continues, contributing to ongoing efforts to enhance electrical safety worldwide.
Questions (FAQ) for Electrical Circuit Breakers
- What is a circuit breaker? A circuit breaker is an electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overcurrent or short circuit. It automatically interrupts the flow of electricity when it detects a fault in the system.
- How does a circuit breaker work? Circuit breakers work by detecting abnormal currents in a circuit. When an overcurrent or short circuit occurs, the breaker’s internal mechanism is triggered, opening the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity.
- Why are circuit breakers important in electrical systems? Circuit breakers are crucial for electrical safety as they prevent damage to equipment, minimize the risk of electrical fires, and protect against electric shock by interrupting the power supply during faults.
- What types of faults do circuit breakers protect against? Circuit breakers protect against overloads (excessive current), short circuits (abnormal connections), and ground faults (current leakage to the ground).
- What are the common types of circuit breakers? Common types include thermal-magnetic circuit breakers, electronic circuit breakers, and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). Each type serves specific applications and has unique features.
- How do you select the right circuit breaker for a specific application? The selection depends on factors such as the type of circuit, load requirements, and environmental conditions. It’s essential to consider the voltage, current rating, and breaking capacity when choosing a circuit breaker.
- What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse? While both provide overcurrent protection, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping, whereas fuses must be replaced. Circuit breakers are more convenient and cost-effective in the long run.
- How do you reset a tripped circuit breaker? To reset a tripped circuit breaker, first, switch it to the “OFF” position and then back to the “ON” position. If the breaker continues to trip, it may indicate an underlying issue that needs to be addressed.
- Can a circuit breaker fail? Yes, circuit breakers can fail. Common causes include aging, mechanical wear, or manufacturing defects. Regular maintenance and testing are essential to ensure the proper functioning of circuit breakers.
- What is arc fault circuit interruption (AFCI), and why is it important?
AFCI is a technology that detects and responds to dangerous electrical arcs in a circuit. It helps prevent electrical fires caused by arcing faults in wiring, cords, or appliances.
- Do circuit breakers need regular maintenance?
Yes, periodic maintenance and testing are recommended to ensure the reliable operation of circuit breakers. This includes checking for signs of wear, verifying connections, and testing the tripping functionality.
- Can I use a circuit breaker as an on/off switch for appliances?While circuit breakers can be used to disconnect power, they are not designed for frequent on/off switching. It’s better to use a dedicated on/off switch for appliances.
Always consult with a qualified electrician for specific questions related to your electrical system and ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations.
If any mistake found, please write in the comment section.