Working at heights is one of the most hazardous activities in construction and industrial sectors. Falls from elevation are a leading cause of workplace fatalities worldwide. To mitigate these risks, safety nets are widely used as a passive fall protection system. Unlike personal fall arrest systems, safety nets provide collective protection, safeguarding multiple workers at once.
This guide, developed using IS 11057:1984 – Industrial Safety Nets and OSHA’s Fall Protection Standards, provides detailed instructions for the selection, installation, and maintenance of safety nets.
Contents
1. Purpose of Safety Nets
- Provide fall protection for workers at heights where other systems (guardrails, harnesses) are not feasible.
- Prevent serious injuries by absorbing the energy of a fall.
- Offer a collective protection system that covers large working areas (e.g., construction of bridges, buildings, and industrial plants).
2. Relevant Standards
- Indian Standard: IS 11057:1984 – Specifies requirements for industrial safety nets, including material, design, and performance.
- OSHA 1926.105 (Fall Protection in Construction) – Requires safety nets when workplaces are more than 25 feet (7.5 m) above ground and other fall protection is not practical.
- OSHA 1926 Subpart M – Details testing, installation clearances, and performance requirements.
3. Materials and Construction (As per IS 11057:1984)
- Netting Material: High-tenacity synthetic fibres (polyamide, polypropylene, or polyester).
- Cord Diameter: Minimum 12 mm for border ropes; mesh ropes not less than 6 mm.
- Mesh Size: Typically 100 mm × 100 mm (OSHA requires openings small enough to prevent fall-through).
- Knotting: Square mesh with secure knots to prevent unraveling.
- Strength Requirement: Must withstand a drop test using a 100 kg sandbag dropped from 7 meters without rupture.
4. Installation Guidelines
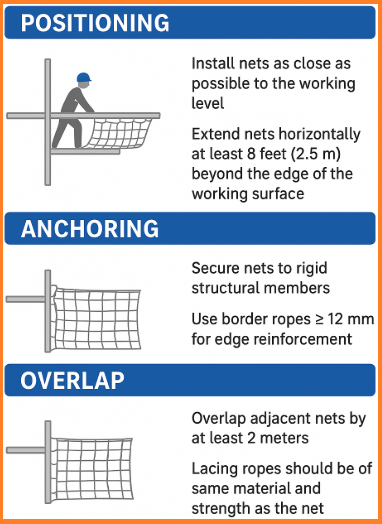
A. Positioning
- Install nets as close as possible to the working level (OSHA allows maximum vertical distance of 30 feet (9.1 m) below the work surface).
- Extend nets horizontally at least 8 feet (2.5 m) beyond the edge of the working surface.
B. Clearances
- Ensure sufficient clearance below the net so that workers falling into the net do not strike underlying surfaces (OSHA specifies testing by dropping a 400 lb [~180 kg] sandbag from intended fall height).
C. Anchoring
- Nets must be secured to rigid structural members.
- Use border ropes (≥12 mm) for edge reinforcement.
- Anchorage spacing should not exceed 2.5 m (IS 11057).
D. Overlaps
- Adjacent nets must be overlapped by at least 2 meters to prevent gaps.
- Lacing ropes should be of the same material and strength as the net.
5. Inspection and Maintenance
A. Before Installation
- Verify certificate of conformity to IS 11057 / OSHA drop-test requirements.
- Check for cuts, abrasions, or UV degradation.
B. During Use
- Inspect nets daily for damage.
- Ensure knots remain tight and intact.
- Replace nets if exposed to chemical contamination, heat, or severe mechanical impact.
C. Periodic Testing
- OSHA requires periodic drop tests with a sandbag (400 lbs) unless certified by the manufacturer for equivalent performance.
- IS 11057 specifies impact absorption tests as per the drop height.
6. Best Practices for Safe Use
- Do not allow debris or materials to accumulate in nets.
- Train workers on proper use and limitations of safety nets.
- Use in conjunction with other systems (guardrails, lifelines) where possible.
- Maintain records of inspections and tests.
7. Comparison: IS 11057 vs. OSHA Requirements
| Parameter | IS 11057:1984 (India) | OSHA 1926 (USA) |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test Load | 100 kg sandbag from 7 m | 400 lb (180 kg) sandbag from intended fall height |
| Maximum Installation Below Work Surface | Not specified, but “as close as possible” | 30 ft (9.1 m) |
| Horizontal Extension | 2.5 m minimum | 8 ft (2.5 m) minimum |
| Mesh Size | 100 × 100 mm | Small enough to prevent fall-through |
| Border Rope Diameter | ≥12 mm | Equivalent strength ropes |
| Overlap Requirement | ≥2 m | Not explicitly mentioned |
Safety nets are lifesaving passive protection system when installed and maintained correctly. By following the technical requirements of IS 11057:1984 and OSHA 1926 standards, industries can ensure effective fall protection, prevent fatalities, and maintain compliance with global safety benchmarks.
Employers should remember that installation must always be carried out under supervision of competent persons, with proper training, inspection, and certification.





