Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP) is a structured and systematic approach used to identify potential hazards and operational issues in industrial processes. It is widely applied in chemical, petroleum, and other process industries to enhance safety and efficiency. By analyzing deviations from the design intent, HAZOP helps mitigate risks and ensures that processes operate within safe limits.
Contents
Deviation from Design Intent
In a HAZOP study, deviations from the intended design are analyzed using a combination of guide words and process parameters. This approach allows the team to systematically assess potential risks that may arise due to abnormal conditions.
Guide Words and Process Parameters
The analysis is conducted using specific guide words and process parameters:
- Guide Words: High, Low, More, Less
- Process Parameters: Pressure, Temperature, Flow
By applying guide words to process parameters, possible deviations can be identified. For example:
- High Pressure: Could indicate overpressure leading to equipment failure or leaks.
- Low Temperature: May cause solidification of process fluids or reduced reaction efficiency.
- More Flow: Might result in excessive product wastage or flooding of a vessel.
- Less Flow: Can lead to insufficient cooling or starvation of downstream processes.
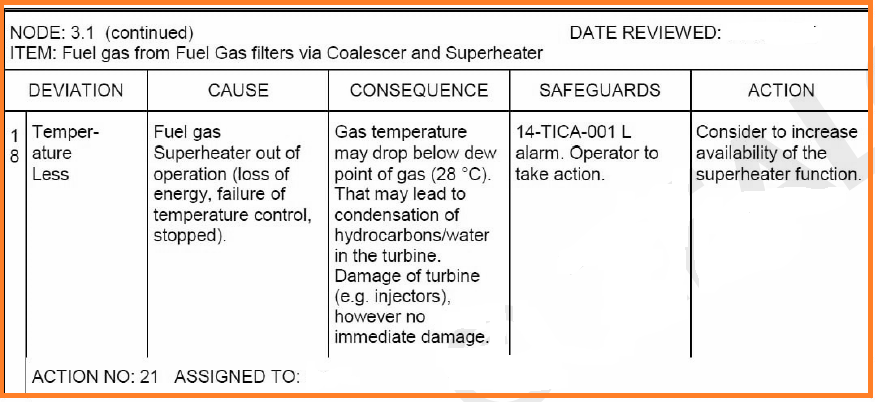
HAZOP Process: Dividing into Nodes
To effectively analyze an entire process, it is divided into smaller components called nodes. A node represents a section of the process where specific parameters are assessed. This breakdown ensures a detailed and focused review, making it easier to identify risks associated with each part of the system.
Safe Design and ALARP Principle
One of the key objectives of HAZOP is to ensure that the process design is inherently safe. The concept of As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP) is used to determine whether risks are minimized to an acceptable level. This principle involves balancing risk reduction measures with cost and feasibility, ensuring that safety is maximized without excessive financial or operational burden.
HAZOP Team and Reporting
A HAZOP study is conducted by a multidisciplinary team comprising process engineers, safety experts, operations personnel, and other relevant stakeholders. The team is led by a HAZOP Team Leader, who is responsible for guiding discussions, ensuring thorough analysis, and documenting findings.
After the study is completed, the HAZOP Team Leader prepares a comprehensive report detailing:
- Identified deviations and potential hazards
- Possible causes and consequences of deviations
- Recommended corrective actions to mitigate risks
- Actions required to achieve ALARP
This report is shared with relevant stakeholders, including management, operations, and regulatory authorities, to ensure proper implementation of safety measures.
HAZOP is a crucial methodology for maintaining process safety and operational efficiency. By systematically analyzing deviations from the design intent, organizations can proactively identify risks and implement necessary controls. Through a structured approach, a dedicated team, and adherence to ALARP principles, HAZOP contributes to safer and more reliable industrial processes.





