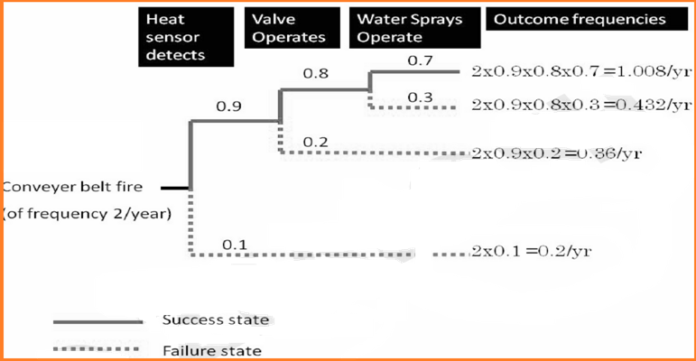
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) is a systematic, graphical method used to evaluate the consequences of an initiating event in a system. It is a forward-looking, inductive risk assessment technique that analyzes the progression of events following an undesired incident. ETA is widely employed in safety and reliability engineering to assess the performance of safety barriers and mitigation measures.
Contents
Key Characteristics of Event Tree Analysis
- Initiating Event: The analysis begins with an undesired event, referred to as the “initiating event.” This event sets off a chain reaction that can lead to multiple potential outcomes.
- Forward Approach: ETA uses a forward-looking methodology, meaning it starts from the initiating event and examines all possible consequences by following various branches of event progression.
- Inductive Analysis: ETA employs an inductive approach, analyzing specific scenarios to predict potential system failures or successes.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis: ETA can be used both qualitatively, to understand the nature of risks, and quantitatively, to calculate probabilities and estimate the likelihood of different outcomes.
- Bottom-Up Approach: ETA builds from the initiating event and systematically examines how different system components respond to it.
- Consequence-Based Analysis: The primary focus of ETA is on the consequences of system failures or successes in response to the initiating event.
- Binary Outcomes: ETA evaluates whether a safety function succeeds or fails at each stage, leading to a set of possible end states.
Event Tree Construction Process
- Define the Initiating Event: Identify the undesired event that sets the process in motion.
- Identify Safety Barriers and Mitigation Measures: List all safety functions designed to control or mitigate the event.
- Develop the Event Tree: Construct a branching diagram where each safety function either succeeds or fails.
- Assign Probabilities (if performing a quantitative analysis): Estimate the likelihood of success or failure for each safety function.
- Analyze Outcomes: Determine the potential end states, including best-case and worst-case scenarios.
- Evaluate and Interpret Results: Use the analysis to identify weaknesses in the system and recommend improvements.
Applications of Event Tree Analysis
- Nuclear Power Plants: Assessing the effectiveness of emergency shutdown systems.
- Aerospace Industry: Evaluating failure scenarios in aircraft operations.
- Chemical and Process Industries: Analyzing potential hazardous material releases.
- Transportation Safety: Assessing safety barriers in rail, road, and maritime transport systems.
Event Tree Analysis is a powerful tool for assessing risks and enhancing system reliability. By systematically mapping out potential outcomes of an initiating event, ETA helps organizations improve safety measures, optimize risk management strategies, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Its structured, consequence-based approach makes it an essential technique in safety engineering and reliability analysis.