A Work Permit System (WPS/PTW) is a formal, written, and structured process designed to control high-risk work activities by ensuring that hazards are identified and managed before work begins. The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) under IS 17893:2023 provides a comprehensive Code of Practice for implementing and maintaining an effective permit-to-work system in industries, construction sites, and other workplaces.
This system acts as a control mechanism between management, supervisors, and workers to ensure that hazardous activities are carried out safely and under strict authorization.
Contents
Objectives of the Work Permit System
- To identify hazards before starting work.
- To ensure that control measures are in place.
- To define roles and responsibilities clearly.
- To prevent unauthorized or unsafe work.
- To establish accountability through documentation.
- To comply with legal and statutory safety requirements.
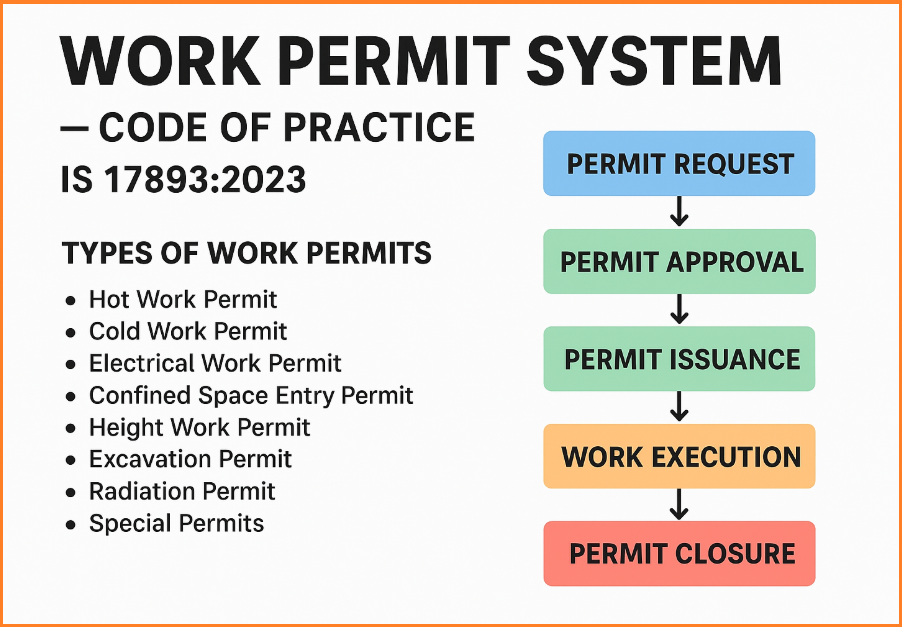
Types of Work Permits
The Code of Practice specifies different permits depending on the nature of work:
- Hot Work Permit – For welding, gas cutting, grinding, or any activity involving heat, sparks, or flames.
- Cold Work Permit – For jobs not involving heat but requiring strict supervision (e.g., mechanical jobs, pipe fitting).
- Electrical Work Permit – For work on live electrical panels, switchgear, or high-voltage equipment.
- Confined Space Entry Permit – For work inside tanks, sewers, manholes, silos, or other enclosed spaces.
- Height Work Permit – For tasks at elevated locations where fall protection is necessary.
- Excavation Permit – For digging, trenching, or construction work below ground level.
- Radiation Permit – For activities involving radioactive materials or radiography testing.
- Special Permits – For jobs that do not fall under the above but involve significant risk (e.g., chemical handling, demolition).
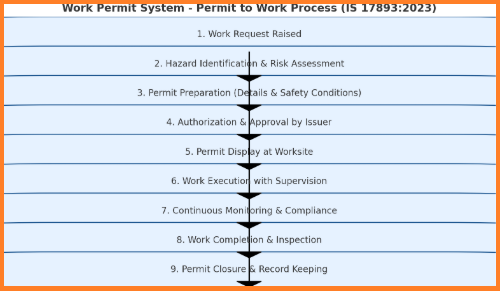
Key Elements of a Work Permit System
- Permit Initiation
- Request raised by a competent person before starting hazardous work.
- Includes job description, location, hazards, and control measures.
- Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment
- Identifies potential risks such as fire, explosion, toxic exposure, or falls.
- Ensures proper control measures like PPE, ventilation, fire watch, and barricading.
- Authorization & Approval
- Issued by an authorized person.
- Specifies duration of validity, scope of work, and safety precautions.
- Permit Display
- A copy of the permit is displayed at the job site for awareness.
- Monitoring During Work
- Continuous supervision to ensure compliance with safety requirements.
- Conditions are checked periodically to avoid unsafe practices.
- Permit Closure
- Work completion verified.
- Site inspected to ensure it is safe for normal operations.
- Permit signed off and recorded.
Roles and Responsibilities
- Employer / Management – Establish the system, provide training, and enforce compliance.
- Permit Issuer – Conducts hazard assessment, issues permits, and ensures safety measures.
- Permit Receiver / Supervisor – Ensures workers follow all conditions of the permit.
- Workers – Carry out tasks safely, use PPE, and immediately report unsafe conditions.
- Safety Officer – Audits permits, ensures adherence, and maintains records.
Documentation & Record Keeping
- All permits must be numbered, logged, and archived.
- Expired and cancelled permits should be retained for audit and compliance checks.
- Digital permit systems can be used for better traceability.
- Reduces workplace accidents.
- Ensures accountability and discipline.
- Enhances communication between teams.
- Complies with statutory requirements (OSHA, BIS, Factories Act, etc.).
- Builds a strong safety culture.
Advantages of Work Permit System
The Work Permit System — Code of Practice (IS 17893:2023) provides organizations with a structured framework to manage hazardous work activities effectively. By defining responsibilities, ensuring authorization, and monitoring safety measures, this system plays a critical role in preventing accidents and protecting workers’ lives.
Adopting this code is not just a regulatory requirement but also a proactive safety management practice that builds trust, discipline, and resilience within organizations.





If any job required for maintenance on high voltage machinery, Before issuing SWP , Electrical isolation must be ensure & LOTO Tag No. should be mansion on SWP. So that their should not be any chance of incident.
Very good article. But in present environment industries are following E-Permit, So there are advantages and dis-advantages in E-PTW, Your comments please.
https://rlsdhamal.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-e-permit-system/