Meaning:
The term ‘organization’ is used in management in different ways as under-
- It refers an activity, process or function of management i.e. organizing.
- It is used in a dynamic way referring to a process by which the structure is created maintained and used.
- It is used in a static way referring a static structure (skeleton) of responsibilities -and authorities is. a network & relationships among individuals-and positions in an organization.
- It refers to an ongoing business unit i.e. a unit which is purposefully created to attain some objectives with resources.
Definitions
- Joseph L. Massie – Organization is defined as the structure and process by which co-operative group of human beings allocates its tasks among its members, identifies relationship and integrates its activities towards common objectives.
- McFarland – It is an identifiable group of people contributing their efforts towards the attainment of goals.
- Haimann – Organizing is the process of defining and grouping the activities of the enterprise and establishing the authority relationships among them, in performing the organizing function, the manager defines, departmentalizes and assigns activities so that they can be most effectively executed.
- Chester Barnard – It is a system of co-operative activities of two or more persons.
- L .Urwick – Organization is the process of dividing up of the activities which are necessary to any purpose and arranging them in groups which are assigned to individuals.
- John Pfiffner – It is essentially a matter of relationship of man to man, job to job and department to department.
- Mooney & Reily – It is the form of every human association for the attainment of a common purpose.
- Kimball & Kimball – Organization is subsidiary to management. It embraces the duties of designating the departments and personnel that are to carry on the work, defining their functions and specifying the relations that axe to exist between departments and individuals.
- Louis Allen – Organization is a process of (i) identifying and grouping the work to be performed (ii) defining and delegating responsibility and authority and (iii) establishing relationships for the purpose of enabling people to work most effectively together in accomplishing objectives.
- G. R. Terry – Organizing is (i) the establishing of effective behavioural relationships among persons (ii) so that they may work together efficiently and (iii) gain personal satisfaction in doing selected tasks (iv) under given environmental conditions (v) for the purpose of achieving some goal or objectives.
- Johnson, Kast and Resnzweig – Organization is an assemblage of people, materials, machines and other resources geared to task accomplishments through a series of interaction and integrated into a social systemic main points that follow from above definitions of organization are
- A business unit is divided into different sections or departments.
- Each section or department is assigned a definite function or duty.
- The authority and responsibility of each section or department or a group of people are clearly defined.
- The interrelationship among various departments and among the groups of people working in them is clearly specified.
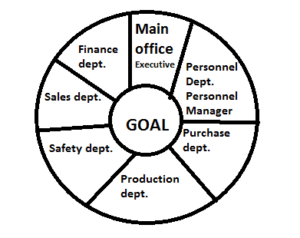
Safety Organization defined: inferring from above general definitions, Safety organization can be defined as the structure and process by which groups of people (employees) are divided into sections or departments, each section or department is assigned specific safety function or duty. Authority and responsibility of everybody is clearly defined and interrelationship between them is specified for the accomplishment of organizational safety goals.
A large unit may have safety department which may have groups of people for division of such safety function and responsibilities. But in a small unit (majority) if such division is not possible and only a few persons are available for safety work, they will be assigned specific duty and other departmental heads (production, purchase, personnel etc.) will be explained their role and responsibility towards safety goals. All supervisors shall be integrated with safety as part of their duty. ‘Safety is everybody’s duty’ will be explained to all with their safety duty given in writing or by displaying at their workplaces.
Need (Significance) of Organization
Organization is the foundation or framework of the whole structure of management and contributes greatly to success and continuity of an enterprise in the following ways
- Facilitates administration and other functions of management process.
- Facilitates growth and diversification.
- Permits optimum use of technological improvements.
- Encourages use of human beings.
- Stimulates creativity.
- Attains maximum efficiency with minimum costs.
Planning is the brain of a business unit while organization is its physical structure. All managerial functions like planning, directing, co-coordinating, controlling, budgeting, staffing etc. are performed through the medium of organization.
Its importance is remarkably explained by Andrew Carnegie (American industrialist) “Take away our factories; take away our trade, our avenues of transportation, our money. Leave us nothing but our organization, and in four years we shall have re-established ourselves”.
Nature (characteristics) of Organization: Briefly can be stated as under-
- It is a set up to realize the objectives (common purpose).
- It is a co-operative activity.
- It is a process (function) and structures both.
- Division into Departments or groups. Division of labour.
- Delegation of authority and responsibility. The chain of superior subordinate relationship is known as ‘chain of command’.(Authority structure).
- Importance of human element (people).
- Vertical and horizontal relationship between man to man, job to job and department to department.
- It is closely linked with planning. Other functions of management are not possible without organization.
- It is flexible and accommodates environmental changes.
- It is stable and resists challenges.
- Provides supervision, control and review. Provides mechanism of co-ordination.
- Provides channels of communication.
- Provides policies, procedures, rules and regulations for systematic functioning.
- Backbone f management and regenerates everything from beginning.
Principles of Organization (Features of a good Organization Structure):
They are summarized as under-
- Unity of objective – all are geared to common objectives.
- Span of control – each superior has limited subordinates to report him.
- Unity of command – each subordinate has only one superior to get command.
- Scalar principle – clear chain of command from top to bottom.
- Co-ordination – should exist among all individuals and groups.
- Communication should be open and clear.
- Facilitates leadership.
- Parity of authority and responsibility – exist by way of delegation.
- Exception principle – only matters beyond control may be referred to higher levels.
- Functional definition – Functions (duties), authority and responsibility of every position should be clearly defined so as to avoid duplication or overlapping.
- Efficiency – optimum use of resources at minimum possible costs.
- Flexibility – should accommodate changes.
- Stability – should resist challenges.
- Continuity – by training and development of executives and employees.
- Balance – between centralization and decentralization
- Division of work – one member one function.
- Unity of direction – clear-cut directional all levels. Directions should be simple, easy. to understand and unambiguous.
- Simplicity and clarity they add to efficacy of origination.
Types of Organization:
There are seven types of organization
- Line, military, scalar or vertical organization.
- Line & staff organization.
- Functional organization.
- Product organization.
- Project organization.
- Matrix organization, and
- Committees.
In ‘Line organization’ line of authority is vertical flowing from top to the bottom and no staff specialists. In Functional organization’ the whole task is divided into specialized function (departments) and horizontal relationships also exist.
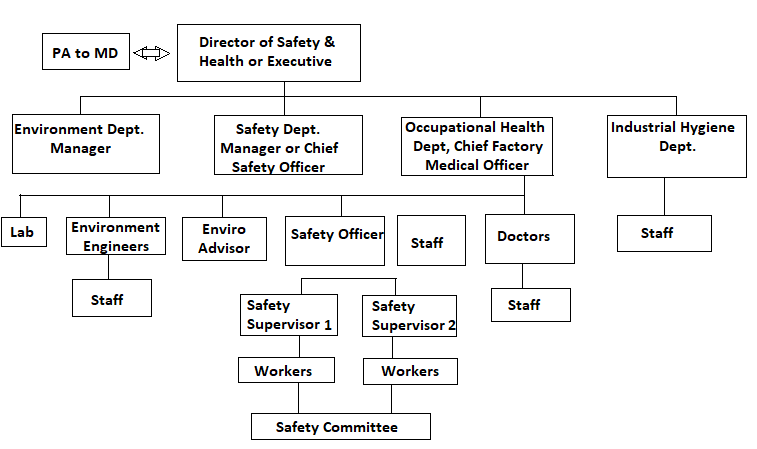
Line & Staff Organization:
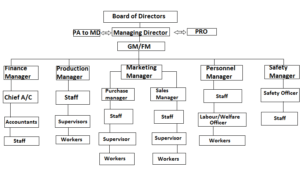
‘Line & staff organization’ is a combination of line and functional structures, line of authority flows in a vertical line, Nit staff specialists are attached to line positions to advise them on important matters and these specialists do not have power of command over subordinates in other departments, but they possess it over subordinates in their own department e.g. Chief Safety Officer has command over safety officers in his department but he has no command over accounts officer in other department. He has only advisory relationship with other departments like production, personnel, HRD etc.
Line & Staff Function of Safety:
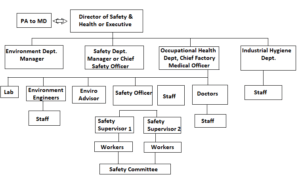
Director or Safety & Health Executive is at the top of the line of authority. He has PA for assistance. Under him there are Managers for Safety, Occupational Health, Industrial Hygiene and Environment departments. They are reportable to Director but not to each other. They may consult or advice each other but cannot compel work. Safety Manager has Safety Officer(s) with staff. They have Safety Supervisors under them who supervise their respective areas and workers allotted to them. Similarly Health department has doctors under them with OHC. Environment dept has environment engineers, lab and staff.