Management Information System (MIS) has become a powerful tool for industry, trade and business in the modern world. It should be user-friendly and easy to understand.
With the Age of Computers, the speed, capacity, accuracy and a variety of uses of Information has been tremendously increasing in almost all walks of life.
Computers are useful not only for strong information but also for generating data, designing, programming, processing, controlling, running robots and microprocessors, communication, developing science, technology and management systems, analyzing and using information, forecasting and personal use.
CLICK HERE FOR > Computer Application use in safety management
We have entered the age of internet, web-site and information highways. The information (data-processing) must be accurate, pertaining to the point, concise, updated, meaningful, trust worthy and as per the need of the user.
The area of Safety, Health & Environment has also been delighted by an entry of computers and internet.
The huge amount of information on accident statistics, health data and environmental aspects can, now, be easily stored, analyzed, transmitted and used for many purposes.
However, in our country the use of computers for these areas is yet to be developed in majority of factories, particularly in medium-scale and small ones.
Software should be developed for information in this vital area of safety, health and environment.
There should be effective MIS between Safety Department and the top management of the company to appraise the work being done by the Department.
CLICK HERE FOR > Advantages and Disadvantages of Computerized System
Similarly, it should also be developed/extended for bottom line management and the outside authorities to provide quick and tabulated information in wide areas of safety, health & environment.
Computer, FAX, Internet, E-Mail and V-mail system can be used to devise various formats, tables, charts, symbols, graphs and documents to report, analyze, reply and store the information pertaining to accidents, statutory requirements, compliance, training programs, safety meetings, future planning, budgeting, monitoring, work permit systems, safety appraisal reports, safety audits etc.
Types of information for safety may be of the following kind:
| Type | Examples | |
| 1. | Operational | Process control, fire protection system, inspection reports, test reports, environmental monitoring, training program etc. |
| 2. | Legal (statutory) | Legal reports, returns, annexure, updated law. |
| 3. | Tactical | Required for immediate need e.g. procurement of safety equipment, assessing training needs, daily reports etc. |
| 4. | Strategic | Required for long term planning e.g. on-site, off-site emergency plan, layout planning. |
Contents
MIS for SMS :
MIS for Safety Management System should be designed as per own need. One general model may be of the following type:

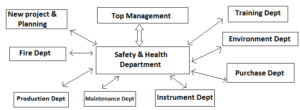
A loop of effective communication system with safety department should be effectively arranged based on existing organization set-up. A simple chart may be as under:
CLICK HERE FOR > Modern Methods of Programming
Sources of Information on Safety, Health & Accidents:
In our country the main sources to get such information are as under:
- The Labour Bureau, Shimla & Chandigarh. Their state offices.
- The Bureau of Indian Standards with its HQ at Delhi, four regional offices and some branches and inspection offices in major cities.
- Loss Prevention Association of India with its offices at Mumbai, Kolkata, Cochin, Hyderabad, Chennai, Delhi and Visakhapatnam.
- National Safety Council with its HQ at Mumbai.
- The Central Labour Institute with its HQ at Mumbai and Regional Labour Institutes (RLI) at Kolkata, Kanpur and Chennai, Faridabad.
- National Institute of Occupational Health (NIOH), Meghaninagar, Ahmedabad-380016.
- The Mahatma Gandhi Labour Institute Thaltej Road, Ahmedabad-380052.
- Ministry of Environment & Forests, New Delhi.
- Safety and Health Information Bureau, Sector 16, Vashi, New Mumbai – 400705.
- Gujarat Safety Council 4th floor, Midway height, beside Panchmukhi Hanuman Temple, Near Kirty mandir, kala Ghoda, Vadodara – 390023.
- The Council of Industrial Safety, Elphinstone Building, 10, Niriman Road Fort, Bombay – 400023.
- The Safety-First Association of India, 2nd floor, Stadium House, Nariman Rd., Fort Mumbai 400023.
- Directorate General of Mines Safety, Dhanbad – 826004, Jharkhand.
- Ahmedabad Textile Industries Research Association (ATIRA), near Gujarat University, Navarangpura, Ahmedabad-380009.
- National Institute of Training for Industrial Engineering, Vihar Lake Rd, Mumbai-400087.
- National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur-440010.
- Indian Association of Occupational Health, C-62, Defence Colony, New Delhi-110024.
- Industrial Health Organization, Babu Vihar, 7/198, Swaroopmagar, Kanpur, UP.
- Department of Industrial Health, Tata Services Ltd., jeevan Vihar, 75, Apollo Street, Fort, Mumbai-400023.
- Industrial Toxicology Research Centre, P.B. No. 80, Lucknow-226001.
- Indian Council of Medical Research, Ansarinagar, Medical Enclave, New Delhi.
- All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, 110, Chittaranjan Avenue, Calcutta-700012.
- Occupational Health Research Institute, C/o BJ Medical College, Ahmedabad-380016.
- Safety, Health & Environment Association, 2nd Floor, Vadilonu Ghar, Kasak Fuvara, Bharuch-392012. Gujarat.
- Kamdar Swasthya Suraksha Mandal, Opp-ESIS General Hospital, Bapunagar, Ahmedabad-380024.
- Vyavsayik Swasthya Suraksha Mandal, 43, Shrinathdham Duplex, Swami Shivanand Road, B/h Dinesh Mills, Vadodara-390007.
- Greentech Foundation, 809, Vishwadeep Tower, Distt Centre. Janakpuri, New Delhi-110058.
- Master of Industrial Hygiene and Safety Division ISTAR Building, Vallabh Vidyanagar, Dist-Anand, Gujarat-388120.
- HSE Information Service, Caerphilly Business Park, Caerphilly CF83 UK.
- Internet, website and computer software are now available on the subjects of industrial safety, health and environment including that of British Safety Council London, National Safety Council USA, CSP (Certified Safety Professional) and CIH (Certified Industrial Hygienist).
CLICK HERE FOR > Compilation, Collation & Analysis of Hazard Information
The publications and periodicals of above institution and Offices of the Labour Departments and Pollution Control Board of various States also provide information on safety, health and environment.
NSC, USA publication ‘Accident Facts’ gives wide information on accident statistics of USA every year.
Some International organizations are as International Labour Organization Geneva, Switzerland (Office in India Sardar Patel Marg, New Delhi).
It has a separate branch for occupational safety and health. For collection dissemination of occupational safety an information, it functions through-
- International Occupational Safety and Health Information Centre (CIS).
- International Programme on C Safety (IPCS) at WHO, HQ, Gene.
- International Occupational Safety Health Hazards Alert Systems. It of the – ILO International Programme, Improvement of Working Condit, Environment (PIAT).
- Clearing House for dissemination information on condition of work ILO publication “Encyclopaedia Occupational Health and Safety” mentioning for its great service information to the world.-
CLICK HERE FOR > SAFETY INDUCTION, EDUCATION, AND TRAINING
World Health Organization (WHO), Switzerland (Office in India at World Health House, Indraprastha Estate, Ring R-Delhi, United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Health and Safety Executive (HSE), Information Centre, Broad Lane, Sheffield 53 7H (UK). There are many other such organizations in many countries of the world.
In addition to law books, standard periodicals and publications (books), research seminar or symposia reports, inspectional reports, accident case studies, meetings of or experts and training programs are also vehicles for the exchange of information safety and environment.
1. What is MIS in Safety Management? Management Information Systems (MIS) in Safety Management refers to the use of technology and information systems to collect, process, and analyze data related to safety in an organization. It helps in making informed decisions to enhance safety practices and prevent accidents.
2. Why is MIS important in Safety Management? MIS in Safety Management plays a crucial role in gathering, organizing, and presenting data related to safety incidents, employee training, equipment maintenance, and more. This information aids management in identifying trends, assessing risks, and implementing effective safety measures.
3. What types of data are managed by MIS in Safety Management? MIS in Safety Management manages a wide range of data, including incident reports, safety training records, compliance data, equipment maintenance logs, emergency response plans, and employee safety performance metrics.
4. How does MIS contribute to the prevention of workplace accidents? MIS facilitates the tracking of safety metrics and performance indicators, enabling organizations to identify potential hazards and take proactive measures to prevent accidents. It also supports the implementation of safety training programs to enhance employee awareness and compliance.
5. What are the key components of an MIS in Safety Management system? Key components include a centralized database for storing safety-related data, reporting tools for analyzing trends, incident management systems, training management modules, and communication tools to disseminate safety information.
6. How can organizations ensure data security in MIS for Safety Management? Organizations can ensure data security by implementing access controls, encryption, regular backups, and secure authentication methods. Compliance with data protection regulations and standards is also essential to safeguard sensitive information.
7. How can MIS improve emergency response in safety management? MIS facilitates quick access to critical information during emergencies, such as contact details, evacuation plans, and safety protocols. It enables real-time communication and coordination, ensuring a more effective response to incidents.
8. Can MIS in Safety Management integrate with other organizational systems? Yes, MIS can integrate with other systems like HR, payroll, and operations to streamline processes. Integration allows for a more comprehensive view of safety-related data and enhances the overall efficiency of safety management.
9. How does MIS support regulatory compliance in safety management? MIS helps organizations stay compliant with safety regulations by tracking and documenting safety practices, training programs, and incident reports. It assists in generating reports for regulatory authorities and ensures that the organization meets legal requirements.
10. How can organizations ensure user adoption of MIS in Safety Management? Ensuring user-friendly interfaces, providing comprehensive training programs, and emphasizing the benefits of MIS adoption in terms of improved safety, efficiency, and compliance can enhance user adoption within the organization.
Implementing MIS in Safety Management is a strategic decision that can significantly contribute to creating a safer work environment and reducing the risks associated with occupational hazards.






Very nice information thanks to RLS human care.
fire safety new MIS FORMET
All articles related to HSE are superb to improve our knowledge.